Methods of Preparation of Phenols
Methods of Preparation of Phenols: Overview
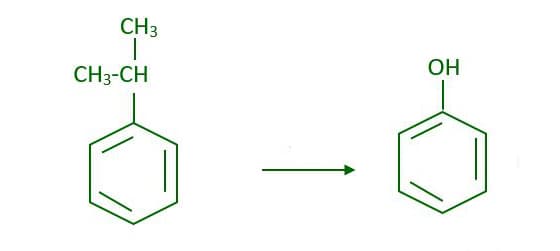
This topic consists of various concepts like Preparation of Phenol by Reaction of Benzene Sulphonic Acid with NaOH,Preparation of Phenol from Cumene,Preparation of Phenol by Fusion of Chlorobenzene with NaOH, etc.
Important Questions on Methods of Preparation of Phenols
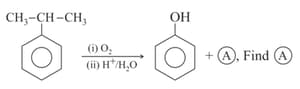
Reagents required to perform the given transformation:
Complete the following reaction :
Show steps to convert nitrobenzene to phenol.
The major aromatic product of the following reaction sequence is
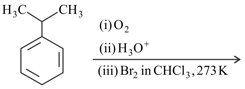
The major product of the following reaction is
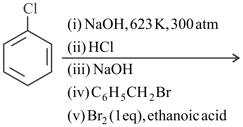
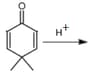
The number of -bonds present inside the ring in the product of above reaction is
Consider the following reaction.
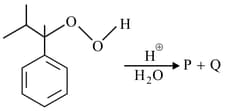
The major products and of the reaction are
Identify the products and of the following reaction:
cumene
In the following reaction
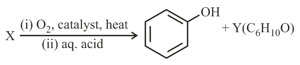
and respectively are:
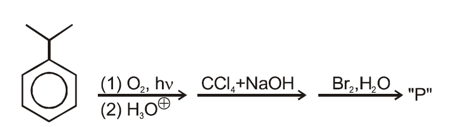
Product contains how many bromine atoms?
The product is
Isopropyl benzene on aerial oxidation followed by acid hydrolysis of the resulting compound yields
What by-product is formed in the process of making phenol from cumene?
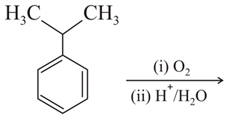
compound is oxidised in the presence of air and subsequent treating with dilute acid to yield phenol and acetone is :
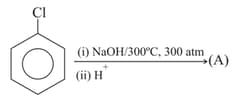
Compound in above reaction is :
Major product (P) of given reaction will not give ?
Which of the following reaction does not give phenol :
In the reaction 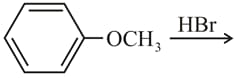 the products are
the products are
Which of the following undergoes hydrolysis most easily :-